For most executives we know, embarking on a transformation journey at the helm of an organization is thrilling. It’s nothing short of an adrenaline rush, like the climbing expedition we’ve been comparing it to over the last few weeks. However, journeys come to an end, and life -as well as business- goes on. Business as usual, they say. At the foot of the mountain, the heroes of the hike blend with ordinary folks and continue onward. That part of the story typically gets left out of the books because… who wants to hear about the ‘normal’? We revive that story here, in the final article of the series, The Next Normal of a New CEO.
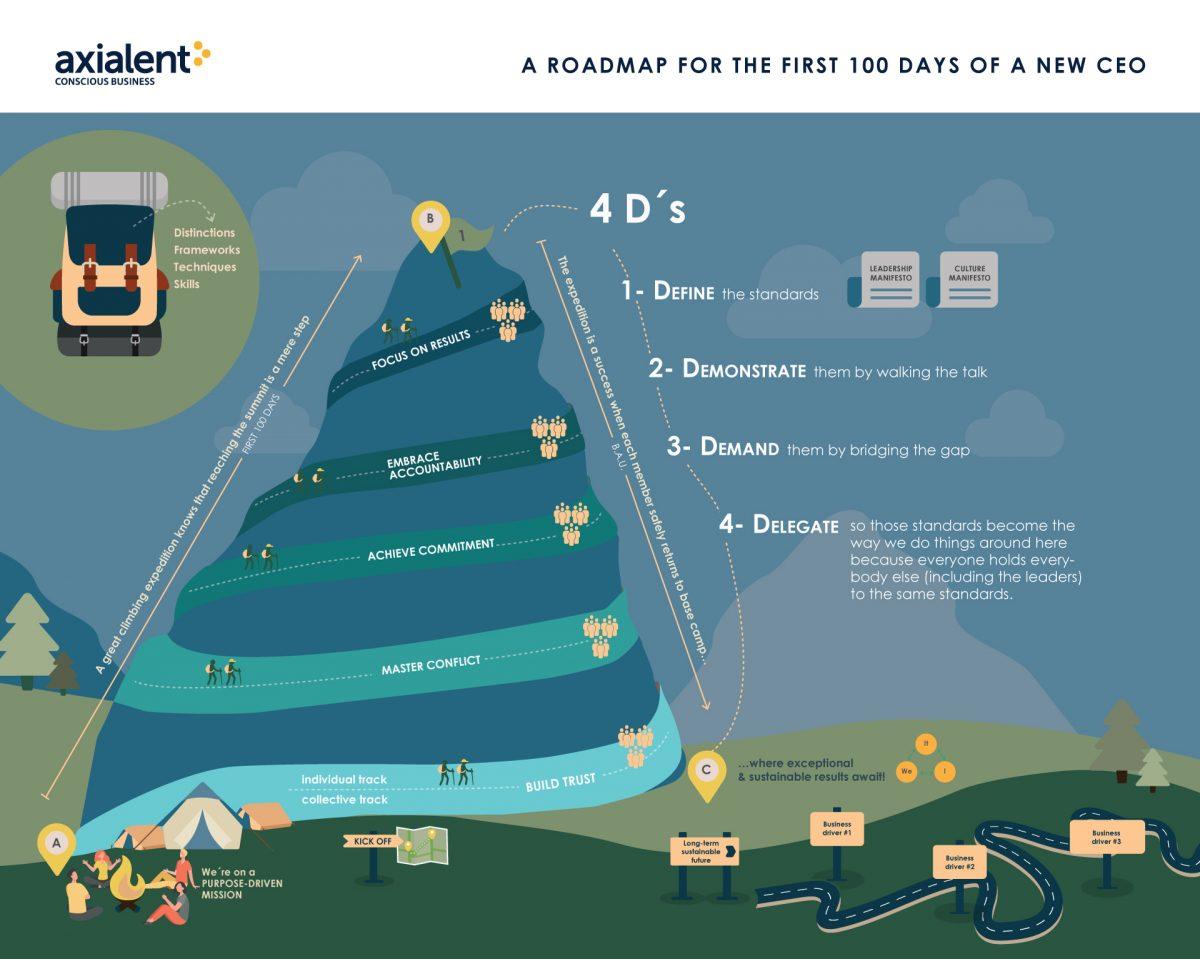
In the first article, we laid out a roadmap for the first 100 days of a CEO and the ‘new’ leadership team that results from that appointment (from A to B in the illustration above). We continued with a second article where we explained the focus of the team’s next 100 days in its safe descent back to base camp (from B to C). We finish the series with the ‘next normal’ of this team (‘new normal’ sounds too definitive for a VUCA world).
 Beginnings, or new beginnings, are exciting. They create momentum, but it’s a hard job to keep the flame alive. If the leadership team does an excellent job with the four D’s mentioned in article two, there’s a higher chance that the flame will last longer. However, they will need a sustainable fuel source for that flame because eventually, it will die out. No matter how well-intended the leaders are, their behaviors are not enough to consolidate an evolving or transforming culture. Culture needs to be hinged on systems to endure.
Beginnings, or new beginnings, are exciting. They create momentum, but it’s a hard job to keep the flame alive. If the leadership team does an excellent job with the four D’s mentioned in article two, there’s a higher chance that the flame will last longer. However, they will need a sustainable fuel source for that flame because eventually, it will die out. No matter how well-intended the leaders are, their behaviors are not enough to consolidate an evolving or transforming culture. Culture needs to be hinged on systems to endure.
Systems and Symbols
What are systems? For us, systems are to the organization what behaviors are to individuals. They are the workflows, procedures, policies, practices (you name it) that shape collective actions. As such, they can be powerful symbols of what the company values, regardless of the words on their posters.
An example of the power of systems and symbols is how top leadership deals with ‘airtime’. What they spend time on, or whom they spend time with, sends a loud message to the organization. Take one of our clients. They decided to end their hierarchical, command-and-control leadership style because their business strategy called for swifter moves that they believed would happen with more autonomous, empowered, and customer-centric teams.
Their leadership manifesto called for them to be ‘servant leaders’. Some took on the challenge of transforming their mindsets and behaviors to become that type of leader. However, their meeting protocols remained unchanged. Front-line employees were still called to provide status updates to top leadership, which meant taking an elevator to the ‘noble’ floor, projecting the same lifeless PPTs as always, as if they were making a case in front of a tribunal waiting for the verdict.
The culture only started shifting when the executives brought the change to another level. No more status updates at the top of the high-rise corporate headquarters. They systematically took the same elevator down, attended the forums where teams did the actual work and asked questions when their turn came. Their leadership manifesto got grounded in their collective rituals, which had a compounding effect on their behaviors.
The Road Ahead
Other systems and symbols in an organization are how the budget is allocated (what do they spend their money on?), whom they hire, who gets promoted, what gets celebrated and punished, and how they reward and discipline. These are the infrastructure on which the leaders keep traveling when they return from their climbing expedition. They arrive eager to reach milestones on their ongoing journey toward long-term, sustainable success in the form of robust business results, healthy relationships, and personal fulfillment. Excellent leadership teams realize that:
-
- The road ahead is full of curves. They will arrive at crossroads where the tools they gathered on their way to the peak will come in handy. The good news is that, after a climb, a curvy road pales in comparison.
- They can’t let their guard down. Continuing to measure how the team is doing on their levels of trust, conflict management, commitment, accountability, and results is paramount for them to keep working out where they are weaker. No matter how well they’re doing, they know that the moment they quit going to the gym, they’ll get out of shape. Staying at the top of their game is a life-long sport.
- They need to get rid of the inappropriate infrastructure that slows their momentum, sometimes to a halt.
- They found their fuel – a healthy fuel that keeps the fire (the one they kindled at the fireside chat at base camp) burning and lighting the way. Holding on to their purpose, their true North, they move not for themselves, but for something that transcends them.
- There is a legacy to leave behind, and they have decided what they want that to be.
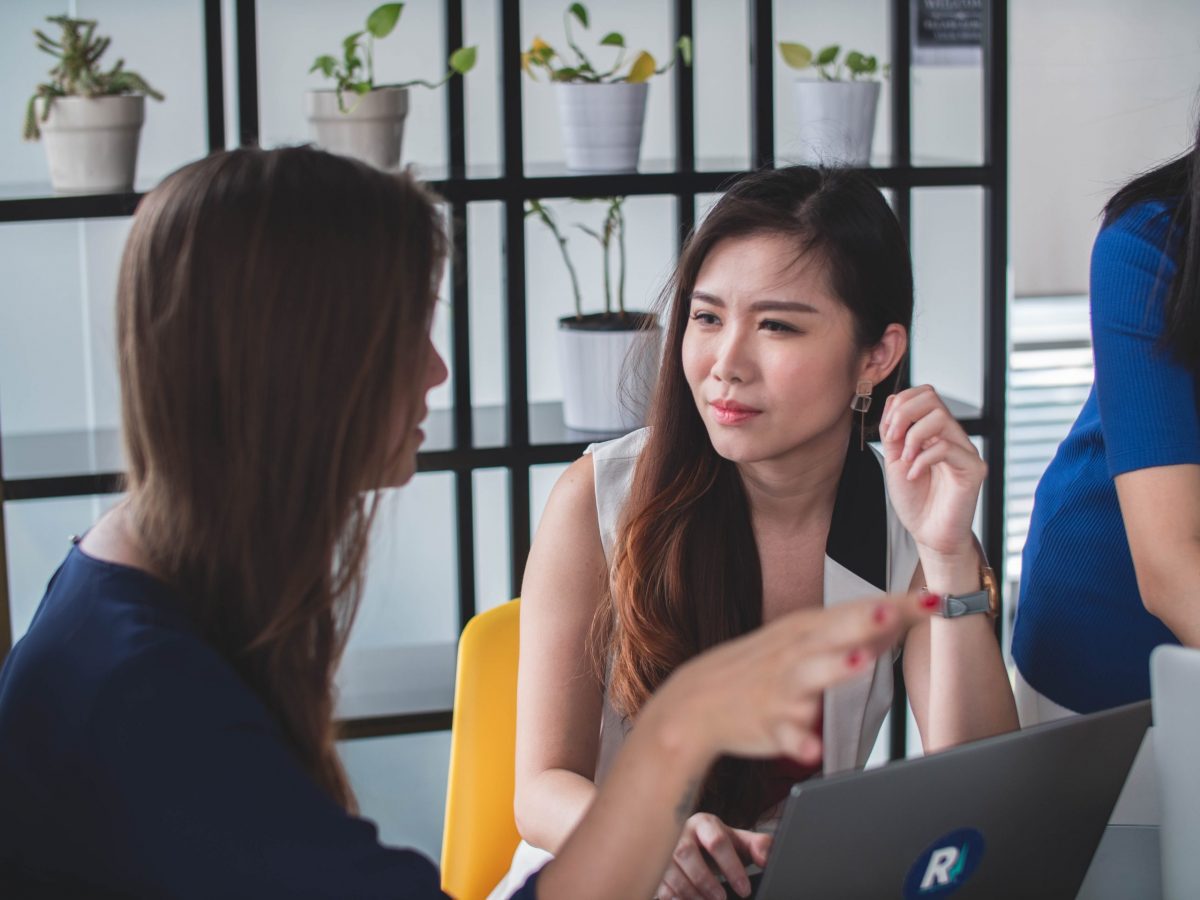

 Compassionate leadership does not mean being “soft with people” and not holding them accountable. It certainly does not propose giving up business results in pursuit of caring for people or make them feel connected. At the heart of compassionate leadership lies the ability to recognize the potential and need of every human being and help them develop and grow in service of the business needs.
Compassionate leadership does not mean being “soft with people” and not holding them accountable. It certainly does not propose giving up business results in pursuit of caring for people or make them feel connected. At the heart of compassionate leadership lies the ability to recognize the potential and need of every human being and help them develop and grow in service of the business needs.
 One of the first outcomes of the leadership team journey described in the
One of the first outcomes of the leadership team journey described in the 


 To whom are we roped?
To whom are we roped? 

 It is about PROACTIVELY CREATING change in uncertain and disruptive environments. Different from resilience, it is about REACTIVELY RESPONDING to change in a constructive way.
It is about PROACTIVELY CREATING change in uncertain and disruptive environments. Different from resilience, it is about REACTIVELY RESPONDING to change in a constructive way.



 The second aspect that made this program different was that it was not designed as the typical immersive, residential, intensive x-day workshop. Instead, we scheduled shorter interventions several weeks apart. This design was deployed before the pandemic, so the sessions were held face-to-face. Nevertheless, this concept has survived to this day as a valid structure for most of our hybrid or purely online leadership development journeys.
The second aspect that made this program different was that it was not designed as the typical immersive, residential, intensive x-day workshop. Instead, we scheduled shorter interventions several weeks apart. This design was deployed before the pandemic, so the sessions were held face-to-face. Nevertheless, this concept has survived to this day as a valid structure for most of our hybrid or purely online leadership development journeys.
 Organizations place a lot of value on leaders who can effectively lead others through change. In fact, effective change leadership is a common competency used to identify and develop high potential employees.2 However, despite the importance that both leaders and organizations place on change leadership, many organizations lack an intentional strategy to help their leaders become effective change-makers. Many of us are guilty of having used the ‘sink or swim’ approach disguised as ‘on the job learning’. Intentionally or not, we throw our up-and-coming talent into leading changes in an environment that is increasingly complex and unpredictable without the benefit of a foundation to help them along the way.
Organizations place a lot of value on leaders who can effectively lead others through change. In fact, effective change leadership is a common competency used to identify and develop high potential employees.2 However, despite the importance that both leaders and organizations place on change leadership, many organizations lack an intentional strategy to help their leaders become effective change-makers. Many of us are guilty of having used the ‘sink or swim’ approach disguised as ‘on the job learning’. Intentionally or not, we throw our up-and-coming talent into leading changes in an environment that is increasingly complex and unpredictable without the benefit of a foundation to help them along the way.
 “Talk” is important. What is communicated about the transformation journey, when aligned with a leader’s behavior, systems, and symbols across the organization, helps accelerate change and enables people to feel part of the journey. The way we tell the story of transformation to ourselves and others can have an inspirational power when connected to a purpose and values.
“Talk” is important. What is communicated about the transformation journey, when aligned with a leader’s behavior, systems, and symbols across the organization, helps accelerate change and enables people to feel part of the journey. The way we tell the story of transformation to ourselves and others can have an inspirational power when connected to a purpose and values.